Making Accessible Website Designs Without Sacrificing Creativity
March 6, 2025
Words by Vev
With Vev, accessible website design doesn't mean compromising on aesthetics.
As a set of rules and best practices, accessibility standards can be interpreted as creatively limiting or restrictive. In this article we provide examples of accessible website designs made in Vev, and a video tutorial on using Vev's accessibility features.
In this article...
Why is accessible website design so important?
First things first, what is “accessible website design”? Web accessibility is, in its simplest definition, the practice of designing for the web so that people with disabilities, such as visual, cognitive, and healing impairments, can easily use and navigate your content.
The importance of web accessibility cannot be understated. From education, employment, and government, to e-commerce, health care, and entertainment, the web is used in almost every aspect of life. For this reason, it is essential the web is accessible to everyone to provide equal opportunity to those with differing abilities.
World Health Organization (WHO) estimates at least 2.2 billion people globally have a vision impairment, and 1 in 6 people experience significant disability of varying forms.

The importance of accessible website design isn't just a choice, in many cases there are minimum legal requirements. It is required by Article 9 of the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) that action is taken to ensure that persons with disabilities can access information and communication technologies on an equal basis with everyone.
On top of this, the business benefits of designing and building for web with accessibility in mind is not to be underestimated. Accessible website design can improve overall user experience, enhance your brand reputation, and grow your market reach, leading to larger audiences, more engagement, and higher conversion rates.
A summary of accessibility standards and requirements
Ensuring website accessibility is crucial for inclusivity and legal compliance. Below is a clear and concise outline of website design accessibility standards and requirements, highlighting minimum legal obligations by country or global market area.
Global Standards
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
Developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), WCAG provides a set of recommendations to make web content more accessible. The guidelines are organized under four principles (POUR):
- Perceivable: Information and user interface components must be presentable to users in ways they can perceive.
- Operable: User interface components and navigation must be operable.
- Understandable: Information and the operation of the user interface must be understandable.
- Robust: Content must be robust enough to be interpreted by a wide variety of user agents, including assistive technologies.
Legal Requirements by Region
1. United States
- Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act: Federal agencies are required to make their electronic and information technology accessible to people with disabilities, incorporating WCAG 2.1 or 2.2 Level AA success criteria.[section508.gov]
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): While not explicitly referencing WCAG, courts have increasingly recognized website accessibility as a requirement under the ADA.[ada.gov]
2. European Union
- Web Accessibility Directive (WAD): Mandates that public sector websites and mobile applications conform to WCAG 2.1 Level AA standards. [Web Accessibility Directive, EU]
- European Accessibility Act (EAA): Extends accessibility requirements to a broader range of products and services, including e-commerce and banking services, to be enforced by June 28, 2025. [European Accessibility Act]
3. United Kingdom:
- Equality Act 2010: Prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities, applicable to websites and online services. [legislation.gov.uk]
- Public Sector Bodies (Websites and Mobile Applications) Accessibility Regulations 2018: Requires public sector websites and mobile apps to meet WCAG 2.1 or 2.2 Level AA standards. It is also a legal requirement to publish an accessibility statement on all public sector websites.
4. Canada:
- Accessible Canada Act (2019): Aims to make Canada barrier-free by 2040, with standards aligning closely with WCAG guidelines.
- Ontario's Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA): Requires public web content to comply with WCAG 2.0 Level AA.
5. Australia:
- Disability Discrimination Act 1992: Interpreted to require web accessibility, with government guidelines recommending WCAG 2.0 Level AA compliance. [legislation.gov.au]
Key Takeaways
- Adopt WCAG Guidelines: Implementing WCAG 2.1 or 2.2 Level AA standards is widely recognized as best practice for ensuring web accessibility.
- Stay Informed on Regional Laws: Accessibility requirements can vary by jurisdiction; ensure compliance with local laws and regulations.
- Regular Audits and Updates: Continuously monitor and update your website to maintain accessibility standards and accommodate new guidelines or legal requirements.
By adhering to these standards and legal requirements, organizations can create inclusive digital experiences and mitigate legal risks associated with non-compliance.
The biggest misconceptions about accessible website design
Myth 1: Accessible website design is a choice
Many still think they can pick and choose when it comes to addressing the accessibility of their website and digital content. As we have seen from the above, this is not the case. In many countries, there is a minimum legal requirement for websites to meet certain accessibility criteria. On top of this, you have a moral obligation as a brand to give everyone equal access to your content.
Myth 2: Accessible website design means function over form
Many feel that they can’t be creatively experimental if they want to adhere to accessibility standards and guidelines. On the other side of the coin, others disregard accessibility entirely in favor of creativity.
The truth? You can get creative and make beautiful digital content that is also accessible. When it comes to creating beautiful web designs filled with bold color and typography choices, and interactivity and animations, using a tool like Vev means you do not have to sacrifice creativity to build an accessible website. Keep reading for tips!
Creative examples of accessible website design in Vev
From bold typography and bright colors, to subtle but powerful animations and microinteractions, here are five examples of accessible web content made using Vev.
Native Advertising Awards 2024 Shortlist
Pfizer
The Big Shift, Deloitte Access Economics and Iress
Dribe
Lolland Energi, Corporate Strategy
Video tutorial: How to create accessible website designs in Vev
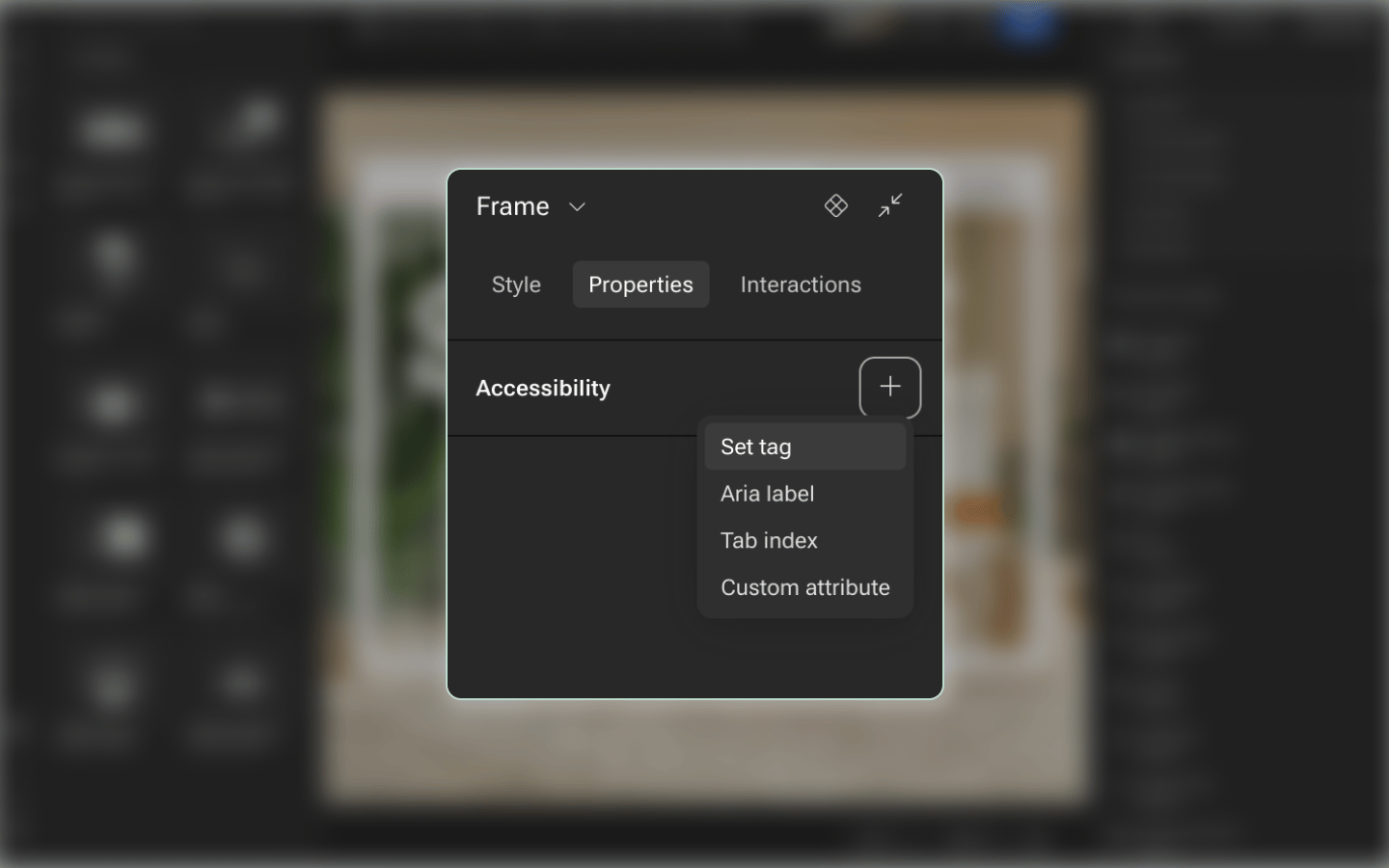
Accessible website design is not just a feature—it's a necessity. Learn how to implement ARIA labels, manage tabindex for better keyboard navigation, and use HTML tags that enhance accessibility across devices.
In this video, we walk you through how to use Vev's Accessibility Editor to make your published content more inclusive and accessible to all users.
📖 Learn more in our help center article, "Making your content accessible".
Create impactful and accessible website designs with Vev
The power of Vev's visual web builder is unmatched when it comes to creative possibilities. On top of this, we have made it easy to add the most common accessibility features, enabling you to create content that is both engaging and accessible to all.